What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Retina is a highly sensitive thin tissue that lines the innermost part of the eye. It is this tissue that gives us our vision and is the part you are using now to read this note. There are tiny blood vessels on the Retina which bring oxygen and nourishment to it. Diabetes damages these blood vessels making them leak blood and fluids into the retinal tissue,thus leading to a condition called Diabetic Retinopathy.
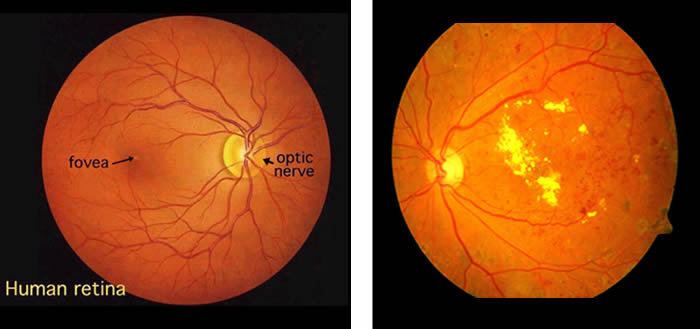
Why is Diabetic Retinopathy Important ?
Diabetic retinopathy, today, has become one of the leading cause of Blindness in the working population. It slowly progresses with time and may not cause symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage.
Who can develop Diabetic Retinopathy ?
Every Diabetic is a potential candidate for developing Diabetic Retinopathy. Longer the person has diabetes, the greater are his/her chances to develop diabetic retinopathy.You are at greater risk if
• Your Diabetes is poorly controlled
• You are on Insulin
• You have had Diabetes for a long time.
How do I know if I have Diabetic Retinopathy ?
Prevention is always better than cure. Hence it is essential to have periodic evaluation of your eye by an Ophthalmologist to detect the condition early..Your pupils may be dilated with eyedrops, so that the Ophthalmologist may have a good look at the back of the eye . Newer modalities of investigations like Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FFA) and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) help in accurately determining the severity of the disease and its treatment.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy treated?
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the disease. Hence early detection of Diabetic Retinopathy is very important. Every Diabetic patient should undergo a proper retina examination at regular intervals. Several treatment options are available for the management of Diabetic Retinopathy like Laser Application to the retina ( Laser PRP ) , certain drugs called Anti VEGFs to be injected into the eye or Vireo-Retinal Eye Surgery in advanced cases. Remember
• Control your blood glucose level.
• See your Ophthalmologist regularly.
• Get advice if you have a problem with your sight.